Carbon emissions of 5G mobile networks in China
Jun 12, 2023·, ,,,,,,·
0 min read
,,,,,,·
0 min read
Tong Li
Li Yu
Yibo Ma
Tong Duan
Wenzhen Huang
Yan Zhou
Depeng Jin
Yong Li
Tao Jiang
 Our Paper.
Our Paper.Abstract
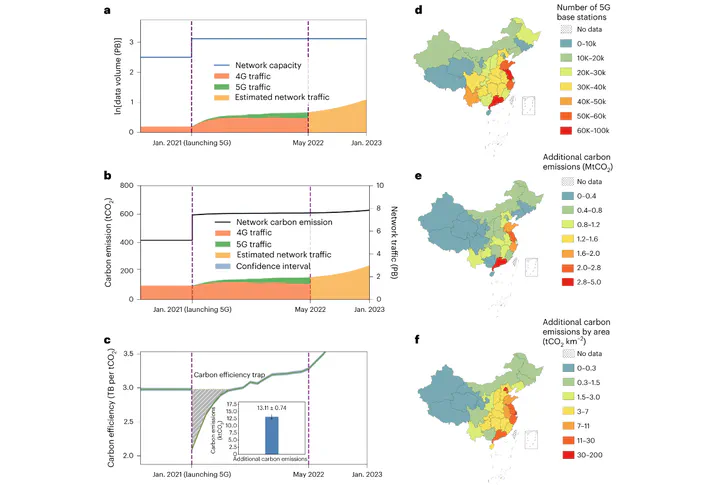
5G telecommunication plays a vital role in our daily life and the global economy. However, the energy consumption and carbon emissions of 5G mobile networks are concerning. Here, we develop a large-scale data-driven framework to quantitatively assess carbon emissions of 5G mobile networks in China, where over 60% of the global 5G base stations are implemented. We reveal a carbon efficiency trap of 5G mobile networks leading to additional carbon emissions of {23.82 $\pm$ 1.07} megatons in China, caused by the spatio-temporal misalignment between cellular traffic and energy consumption in mobile networks. To address this problem, we propose an energy-saving method, called DeepEnergy, leveraging collaborative deep reinforcement learning and graph neural networks, to make it possible to effectively coordinate the working state of 5G cells, which could help over 71% of Chinese provinces avoid carbon efficiency traps. The application of DeepEnergy can potentially reduce {20.90 $\pm$ 0.98} megatons of carbon emissions at the national level in 2023. Furthermore, the mobile network in China could accomplish more than 50% of its net-zero goal by integrating DeepEnergy with solar energy systems. Our study deepens the insights into carbon emission mitigation in 5G networks, paving the way towards energy-efficient and sustainable telecommunication infrastructures.
Type
Publication
In Nature Sustainability